Software Testing Tutorial: Free Course
In this course, you will learn basic skills and concepts of Software Testing. Lessons are taught using REAL-LIFE Examples for improved learning. Refer the tutorials sequentially one after the other.
What should I know?
This online video tutorial is specially designed for beginners with little or no manual testing experience. But before you begin, refer this comprehensive guide on choosing QA as your career
What is Software Testing? Introduction, Definition, Basics & Types
What is Software Testing?
SOFTWARE TESTING is defined as an activity to check whether the actual results match the expected results and to ensure that the software system is Defect free. It involves the execution of a software component or system component to evaluate one or more properties of interest. Software testing also helps to identify errors, gaps, or missing requirements in contrary to the actual requirements. It can be either done manually or using automated tools. Some prefer saying Software testing as a White Box and Black Box Testing.
In simple terms, Software Testing means the Verification of Application Under Test (AUT). This tutorial introduces testing software to the audience and justifies its importance.
In this tutorial, you will learn:
- What is Software Testing?
- Why is Software Testing Important?
- What are the benefits of Software Testing?
- Testing in Software Engineering
- Types of Software Testing
- Testing Strategies in Software Engineering
- Program Testing
Why is Software Testing Important?
Testing is important because software bugs could be expensive or even dangerous. Software bugs can potentially cause monetary and human loss, and history is full of such examples.
- In April 2015, Bloomberg terminal in London crashed due to software glitch affected more than 300,000 traders on financial markets. It forced the government to postpone a 3bn pound debt sale.
- Nissan cars recalled over 1 million cars from the market due to software failure in the airbag sensory detectors. There has been reported two accident due to this software failure.
- Starbucks was forced to close about 60 percent of stores in the U.S and Canada due to software failure in its POS system. At one point, the store served coffee for free as they were unable to process the transaction.
- Some of Amazon's third-party retailers saw their product price is reduced to 1p due to a software glitch. They were left with heavy losses.
- Vulnerability in Windows 10. This bug enables users to escape from security sandboxes through a flaw in the win32k system.
- In 2015 fighter plane F-35 fell victim to a software bug, making it unable to detect targets correctly.
- China Airlines Airbus A300 crashed due to a software bug on April 26, 1994, killing 264 innocents live
- In 1985, Canada's Therac-25 radiation therapy machine malfunctioned due to software bug and delivered lethal radiation doses to patients, leaving 3 people dead and critically injuring 3 others.
- In April of 1999, a software bug caused the failure of a $1.2 billion military satellite launch, the costliest accident in history
- In May of 1996, a software bug caused the bank accounts of 823 customers of a major U.S. bank to be credited with 920 million US dollars.
What are the benefits of Software Testing?
Here are the benefits of using software testing:
- Cost-Effective: It is one of the important advantages of software testing. Testing any IT project on time helps you to save your money for the long term. In case if the bugs caught in the earlier stage of software testing, it costs less to fix.
- Security: It is the most vulnerable and sensitive benefit of software testing. People are looking for trusted products. It helps in removing risks and problems earlier.
- Product quality: It is an essential requirement of any software product. Testing ensures a quality product is delivered to customers.
- Customer Satisfaction: The main aim of any product is to give satisfaction to their customers. UI/UX Testing ensures the best user experience.
Testing in Software Engineering
As per ANSI/IEEE 1059 Testing in software engineering is a method of analyzing a software item to find the differences between current and required conditions. It also involves evaluating the features of the software.
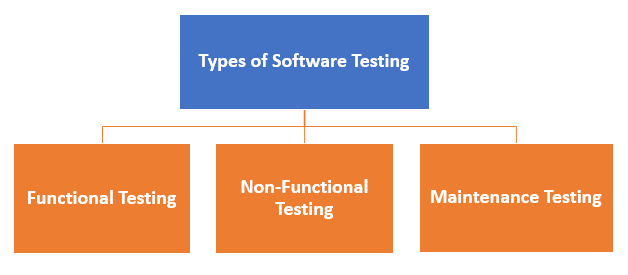
Types of Software Testing
Typically Testing is classified into three categories.
- Functional Testing
- Non-Functional Testing or Performance Testing
- Maintenance (Regression and Maintenance)
| Testing Category | Types of Testing |
|---|---|
| Functional Testing | |
| Non-Functional Testing | |
| Maintenance |
This is not the complete list as there are more than 150 types of testing types and still adding. Also, note that not all testing types are applicable to all projects but depend on the nature & scope of the project.
Testing Strategies in Software Engineering
Here are important strategies in software engineering:
Unit Testing: This software testing approach is followed by the programmer to test the unit of the program. It helps developers to know whether the individual unit of the code is working properly or not.
Integration testing: It focuses on the construction and design of the software. You need to see that the integrated units are working without errors or not.
System testing: In this method, your software is compiled as a whole and then tested as a whole. This testing strategy checks the functionality, security, portability, amongst others.
Program Testing
Program testing is the method of executing any program with the aim of finding errors. A good testing is one which has a high chance of finding bugs. This testing process can show whether the errors are present or not. It is possible to write test cases before writing any program.
Summary of Software Testing Basics:
- Software testing is defined as an activity to check whether the actual results match the expected results and to ensure that the software system is Defect free.
- Testing is important because software bugs could be expensive or even dangerous.
- The important are reasons for using software testing are: cost-effective, security, product quality, and customer satisfaction.
- Typically Testing is classified into three categories functional testing, non-functional testing or performance testing, and maintenance.
- The important strategies in software engineering are: unit testing, integration testing, validation testing, and system testing.
Software Testing as a Career Path (Skills, Salary, Growth)
This guide will take you through the In's and outs of software testing. If you plan to make a career in software testing, this is a MUST READ!
What is Software Testing?
Software Testing is a process of verifying a computer system/program to decide whether it meets the specified requirements and produces the desired results. As a result, you identify bugs in software product/project.
Software Testing is indispensable to provide a quality product without any bug or issue.
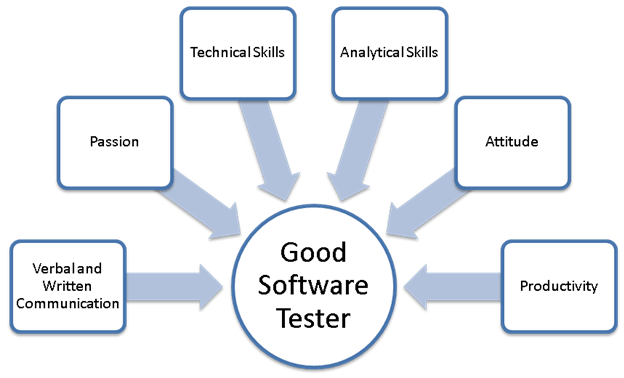
Skills required to become a Software Tester
We will discuss the Technical and Non-Technical required to become a Software Tester
Non-Technical Skills
Following skills are essential to becoming a good software tester. Compare your skill set against the following checklist to determine whether Software Testing is a reality for you-
- Analytical skills: A good software tester should have sharp analytical skills. Analytical skills will help break up a complex software system into smaller units to gain a better understanding and create test cases. Not sure that you have good analytical skills - Refer this link - if, if you can solve at least ONE problem you have excellent analytical skills.
- Communication skill: A good software tester must have good verbal and written communication skill. Testing artifacts (like test cases/plans, test strategies, bug reports, etc.) created by the software tester should be easy to read and comprehend. Dealing with developers (in the event of bugs or any other issue) will require a shade of discreetness and diplomacy.
- Time Management & Organization Skills: Testing at times could be a demanding job especially during the release of code. A software tester must efficiently manage workload, have high productivity, exhibit optimal time management, and organization skills
- GREAT Attitude: To be a good software tester you must have a GREAT attitude. An attitude to 'test to break', detail orientation, willingness to learn and suggest process improvements. In the software industry, technologies evolve with an overwhelming speed, and a good software tester should upgrade his/her technical skills with the changing technologies. Your attitude must reflect a certain degree of independence where you take ownership of the task allocated and complete it without much direct supervision.
- Passion: To Excel in any profession or job, one must have a significant degree of the passion for it. A software tester must have a passion for his / her field. BUT how do you determine whether you have a passion for software testing if you have never tested before? Simple TRY it out and if software testing does not excite you switch to something else that holds your interest.
Technical Skills
This list is long, so please bear with us
- Basic knowledge of Database/ SQL: Software Systems have a large amount of data in the background. This data is stored in different types of databases like Oracle, MySQL, etc. in the backend. So, there will be situations when this data needs to be validated. In that case, simple/complex SQL queries can be used to check whether proper data is stored in the backend databases.
- Basic knowledge of Linux commands: Most of the software applications like Web-Services, Databases, Application Servers are deployed on Linux machines.So it is crucial for testers to have knowledge about Linux commands.
- Knowledge and hands-on experience of a Test Management Tool:Test Management is an important aspect of Software testing. Without proper test management techniques, software testing process will fail. Test management is nothing but managing your testing related artifacts.
For example - A tool like Testlink can be used for tracking all the test cases written by your team.
There are other tools available that can be utilized for Test Management. So, it is important to have knowledge and working experience of such tools because they are used in most of the companies.
- Knowledge and hands-on experience of any Defect Tracking tool- Defect Tracking and Defect life cycle are key aspects of software testing. It is extremely critical to managing defects properly and track them in a systematic manner. Defect tracking becomes necessary because the entire team should know about the defect including managers, developers, and testers. Several tools are used to lock defects including QC, Bugzilla, Jira, etc.
- Knowledge and hands-on experience of Automation tool: If you see yourself as an "Automation tester" after a couple of years working on manual testing, then you must master a tool and get in-depth, hands-on knowledge of automation tools.
Note - Only knowledge of any Automation tool is not sufficient to crack the interview, you must have good hands-on experience, so practice the tool of your choice to achieve mastery. Knowledge of any scripting language like VBScript, JavaScript, C# is always helpful as a tester if you are looking for a job into automation. Few companies also use Shell/Perl scripting, and there is a lot of demand for testers having knowledge of the same. Again, it will depend on the company and which tools are used by that company.
There is also a lot of scope for performance testing tools because applications need to be tested for their performance which is a part of non-functional testing.
That's it to technical knowledge. Please note you do not need ALL the technical skills listed above. The technical skill sets required vary with the Job Role and company processes.
Academic Background
Academic background of a software tester should be in Computer Science.
A BTech/ B.E., MCA, BCA, BSc- Computers, will land you a job quickly.
If you do not hold any of these degrees, then you must complete a software testing certification like ISTQB and CSTE which help you learn Software Development/ Test Life Cycle and other testing methodologies.
Remuneration
Compensation of a software tester varies from company to company. Average salary range of a software tester in the US is $45,993 - $74,935. Average salary range of a software tester in India is Rs 247,315 - Rs 449,111.
Also, a software tester is also given health insurance, bonuses, gratuity and other perks.
What Does a Software Tester do?
On any typical work day, you will be busy understanding requirement documents, creating test cases, executing test cases, reporting and re-testing bugs, attending review meetings and other team building activities.
Software Tester Career Path
Your career progression as a software tester (QA Analyst) in typical CMMI level 5 company will look like following but will vary from company to company
- QA Analyst (Fresher)
- Sr. QA Analyst (2-3 years' experience)
- QA Team Coordinator (5-6 years' experience)
- Test Manager (8-11 years' experience)
- Senior Test Manager (14+ experience)
Alternate Career Tracks as a Software Tester
Once you have got your hand dirty in manual testing, you can pursue following specializations
- Automation Testing: As an Automation Test Engineer, you will be responsible for automating manual test case execution which otherwise could be time-consuming. Tools used IBM Rational Robot, Silk performer, and QTP
- Performance Testing: As a performance test engineer, you will be responsible for checking application responsiveness (time is taken to load, maximum load application can handle), etc. Tools used WEBLoad, Loadrunner.
- Business Analyst: A major advantages Testers have over Developers is that they have an end to end business knowledge. An obvious career progression for testers is to become a Business Analyst. As a Business Analyst, you will be responsible for analyzing and assessing your company's business model and workflows. As a BA, you will intergrate these models and workflows with technology.
Common Myths
Software Testing as a Career pays Less Developers are more respected as compared to Testers
Contrary to popular belief, Software Testers (better known as QA professionals) are paid and treated at par with Software Developers in all "aspiring" companies. A career in Software Testing should never be considered as "second rated."
Software Testing is Boring
Software Testing could actually "test" your nerves since you need to make sense of Business Requirements and draft test cases based on your understanding. Software testing is not boring. What is boring is doing the same set of tasks repeatedly. The key is to try new things. For that matter, have you ever spoken to a software developer with more than 3 years' experience? He will tell you how boring his job has become off-lately.
How to Become Software Tester
For a complete newbie, here is our suggested approach to learning Software Testing
You start with learning Basic principles of Software Testing. Once done you apply for freelancing jobs. This will help you gain practical knowledge and will fortify the testing concepts you have learned.
Next, you proceed to Selenium - Automation tool, then JMeter - Performance Testing tool and finally TestLink - Test Management Tool. All the while you are learning, we suggest you apply for freelancing jobs (apart from other benefits you will make some moolah too!).
Once you are through with all the tools, you may consider taking a certification. We recommend ISTQB. However, this is optional.
Certification Exams:
ISTQB Foundation level is the basic certification in Testing field.
It is not mandatory, but it will help increase your chances of getting the job. Most of the companies have this criterion.
A software tester with ISTQB cleared will be given more priority as compared to others.
After this, when you apply for permanent jobs in big corporations you will have many skills to offer as well some practical freelancing experience which may be of value and will increase your chances of being selected.
You can also pursue certification in a Testing tool of your choice.
Learning Guides: -
- Software Testing Tutorials - link
- Selenium - link As an alternative you can also learn QTP
- Jmeter - link As an alternative you can also learn Loadrunner
- Testlink - link As an alternative you can also learn Quality Center
- Freelancing Jobs – UpWork or Freelancer
- Permanent Jobs - Any major job portal like monster.com or naukri.com
Hope to see you at a QA conference some Day! :-)
Here is a tool to help you make a career choice
click here to know more details of

nice
ReplyDelete